Vortex Dynamics and Losses Due to Pinning: Dissipation from Trapped Magnetic Flux in Resonant Superconducting Radio-Frequency Cavities
Liarte, Hall, Koufalis, Miyazaki, Senanian, Liepe, Sethna
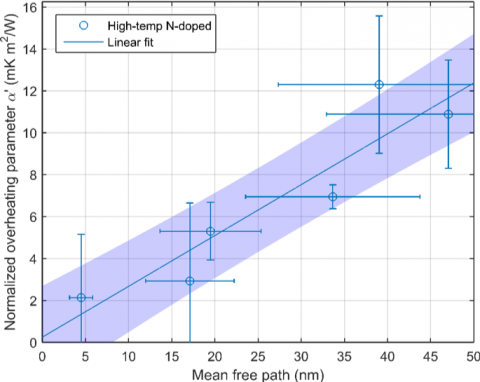
Trapped flux is one of the dominant causes of loss in modern SRF cavities. We use ideas from collective pinning to solve the dynamics of vortices subject to ac magnetic fields and a disordered potential, and guide the tuning of material properties to optimize cavities in particle accelerators. Our theory of elastic strings moving in disordered media describes well experiments in resonant cavities for particle accelerators and can be used to optimize performance. Our work advances the efficiency of Nb and Nb3Sn cavities. Our predictions can be used to guide the production of SRF cavities with higher quality factors and hence lower cryogenic costs.
Full Publication:
https://journals.aps.org/prapplied/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.10.054057