Theoretical descriptions of the anti Q slope of SRF cavities
J. T. Maniscalco and M. Liepe
CBB demonstrated that theoretical descriptions of the anti Q slope of SRF cavities (in which the quality of cavities increases with the RF field) that currently are proposed in literature are based either on incorrect assumptions or incomplete calculations. Using a simple model to estimate the non-equilibrium distribution of the quasiparticles, we corrected these previous calculations and showed that a bonafide theoretical explanation is still lacking. CBB is now working on developing a correct theoretical model.
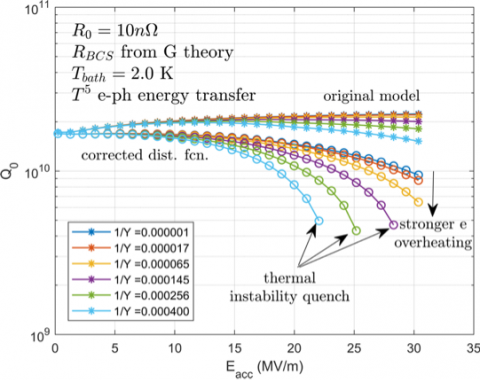
The figure shows the theoretically predicted quality Q0 as a function of the strength of the RF field Eacc for multiple assumptions about the heat transfer rate Y (in W/(K/m^2)) from surface (non-superconducting) electrons to phonons. One set of curves (o) correctly accounts for quasiparticle stimulation over the RF cycle, while the other (*) does not. The corrected calculation fails to reproduce the experimentally observed increase in Q with Eacc.
Full Publication
: http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/AccelConf/ipac2019/papers/weprb089.pdf